Facility management (FM) is a profession that encompasses multiple disciplines to ensure functionality, comfort, safety and efficiency of the built environment by integrating people, place, process and technology.
Your facility manager.
Facility managers (FMs) can have many different titles and arrive in their profession through a variety of career paths. They're responsible for making sure systems of the built environment, or facility, work harmoniously. They are important because they make sure the places in which people work, play, learn and live are safe, comfortable, productive and sustainable.
FMs contribute to the organization’s bottom line through their responsibility for maintaining what are often an organization’s largest and most valuable assets, such as property, buildings, equipment and other environments that house personnel, productivity, inventory and other elements of operation. Here are some of the ways FMs contribute to an organization’s business strategy and bottom line:
The FM industry is growing at a rapid pace and the roles of FMs are broadening to encompass more responsibilities and skill sets. FM budgets and teams are becoming larger and more impactful as the built environment becomes more integral to the ways modern society conducts business, entertainment and lifestyles. Here are a few social trends that are deeply rooted in and affected by facility management:
These are the 11 core competencies of facility management:
Even though FMs don’t always have similar titles, they share common roles within their respective organizations, including:
Set up in April 2018, the tripartite FM Implementation Committee (FMIC) brings together major stakeholders from public and private sectors to enhance service delivery of FM companies and uplift the industry.
To advance the FM industry from a labour intensive industry to a productive one using data analytics, predictive maintenance and smart solutions.
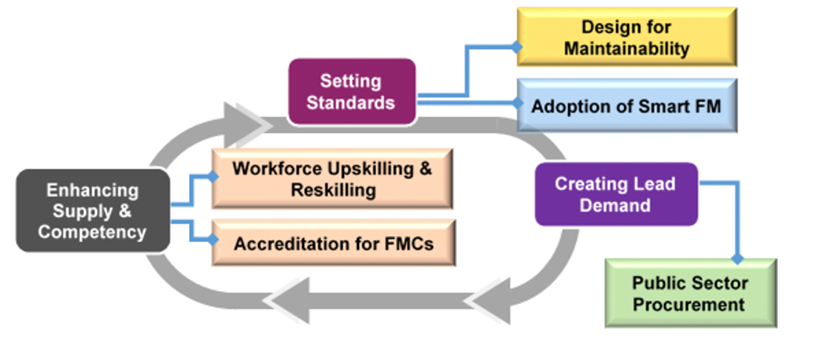
The FMIC has proposed key approaches to target challenges at industry-, firm- and manpower-level.
| Set FM standards | Encouraging adoption of Design for Maintainability Standards for new buildings by having designs that include maintainability considerations and existing buildings undergoing retrofits |
|---|---|
| Government sets lead demand | Government serving as an early adopter through its procurement framework to motivate the FM sector to raise competency. High quality FM services can be achieved by building capability at both firm- and personnel-level, with support from a productive, tech-leveraging workforce. |
| Key recommendation | Details |
|---|---|
| Design for maintainability (DfM) – Include FM considerations in building design stage |
|
| Smart FM – Enhance maintenance capabilities through smart FM to raise productivity, improve quality and reduce FM man-hours |
|
| Manpower and industry development – Ensure the FM workforce receives adequate training and firms are credible through accreditation |
|
Smart Facilities Management (FM) refers to the integration of systems, processes, technologies and personnel to enhance the management of a building's facilities. It is about doing better with technology, using it as a means to an end. It is important to consider the process and people aspect in order to harness the full potential of smart FM and achieve a holistic solution that can support data-driven decisions, create change and improve outcomes.
“Smart FM is about integrating technologies, people and processes to improve communications, lessen response time, reduce costs and manpower and more importantly, raise productivity.” - Tony Khoo, President, Singapore International Facility Management Association (SIFMA)
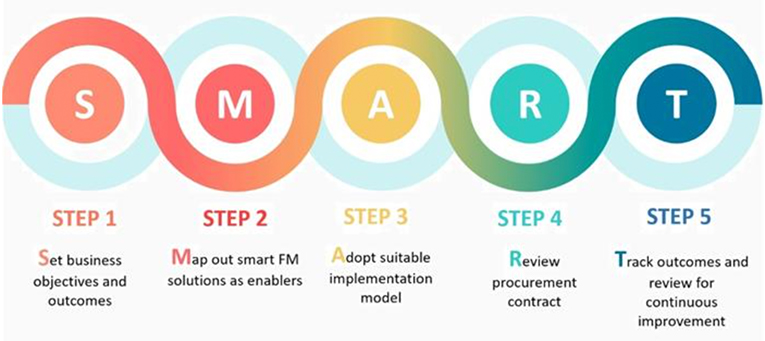
To drive the adoption of smart FM, the Smart FM Taskforce developed a Guide to Smart FM that was launched on 1 October 2019. The Guide aims to provide Building Owners and their FM Managers with an easy-to-use reference to guide them on the key steps to take in their smart FM journey.
The Guide is applicable to various building types and FM operating models, while being mindful that most buildings have a diverse range of systems. Building Owners, FM Managers, FM Companies (FMCs) and Service / Solution Providers can use this Guide and the 5-Step SMART process as follows: